Companies have a significant impact on economies, communities, and individuals within society. Fundamentally, companies supply goods and services to satisfy customer demands while making money and adding value. This blog will examine the foundations of business, including its various forms and global effects, and offer helpful tips for achievement.
Introduction to Business
Business, in its most basic sense, refers to any activity undertaken with the intention of making money. Companies exist to serve consumers with goods and services; in doing so, they promote economic growth, generate jobs, and advance societal advancement.
Why Is Business Important?
Businesses are the foundation of society and are about more than just making money. Through creating jobs, innovating to enhance products, and encouraging competition to improve services, they raise people’s quality of life.

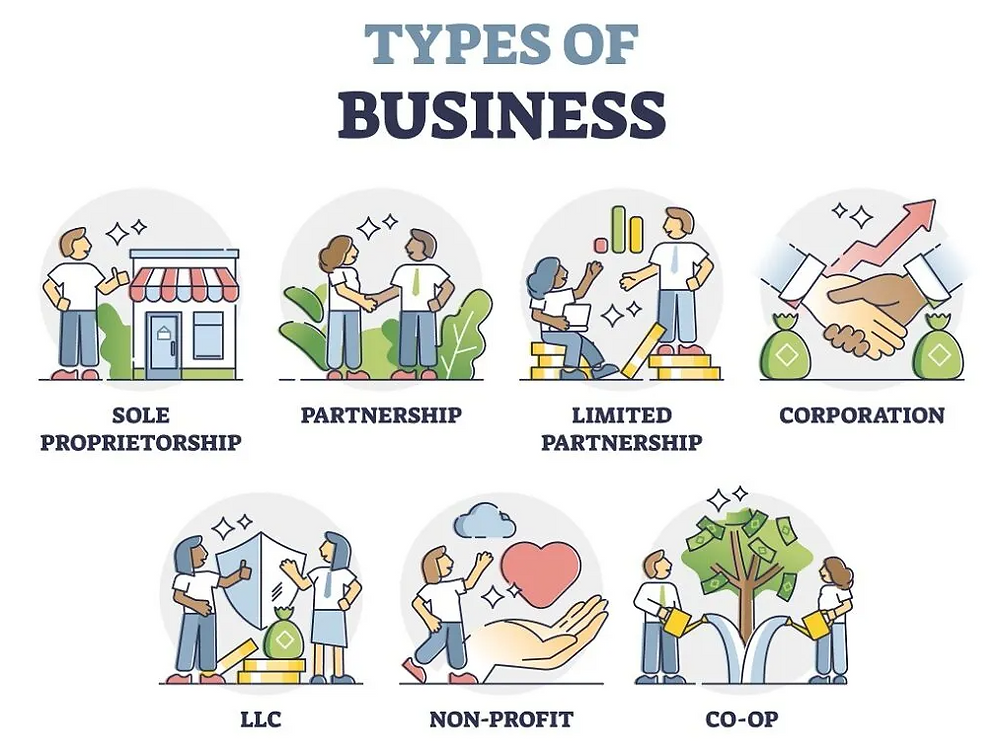
Types of Businesses
Businesses can function in a variety of ways, each with unique benefits and difficulties. The four main categories of businesses are as follows:
Sole Proprietorship
This is the most basic type of business, in which a single person owns and runs the whole enterprise. Although they are simple to set up, sole proprietorships run the danger of personal liability.
Partnership
In a partnership, two or more persons jointly own the company. Shared capital and experience are advantageous for this kind of firm, but conflicts over earnings and management are possible.
Corporation
A corporation is a more comprehensive organisation that exists independently of its owners. Although corporations have less responsibility, they nevertheless have additional regulatory obligations.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC offers flexibility and shields owners from personal liability by combining the advantages of corporations and partnerships.
Objectives of Business
Enterprises function with diverse objectives in mind. While making a profit is the main goal, prosperous businesses frequently set higher goals.
Profit Generation
The primary goal of any business is to turn a profit. Sustainability, growth, and expansion are guaranteed by profitability.
Value Creation for Customers
Businesses that concentrate on giving their clients value usually succeed. Long-term success and repeat business are linked with satisfied customers.
Employment Generation
Companies are essential to the generation of jobs because they give people the chance to make a living and give back to the community.
Social Responsibility
Businesses are paying more attention than ever to how they affect society, from sustainable environmental practices to ethical buying of goods.
Business Models
Depending on its goods or services, a business might run in a variety of ways. Some typical business models are as follows:
Product-Based
This business model entails selling clients physical products, ranging from specialist technology to everyday goods like clothing.
Service-Based
Intangible products like consulting, software development, or house cleaning services are offered by service-based businesses.
Subscription-Based
This business model, which is common in the digital era, charges clients a fixed price for continuous access to a good or service, such as software or Netflix subscriptions.
E-Commerce and Online Models
With the growth of the internet, a lot of companies now only conduct business online, using digital platforms to sell goods and services.
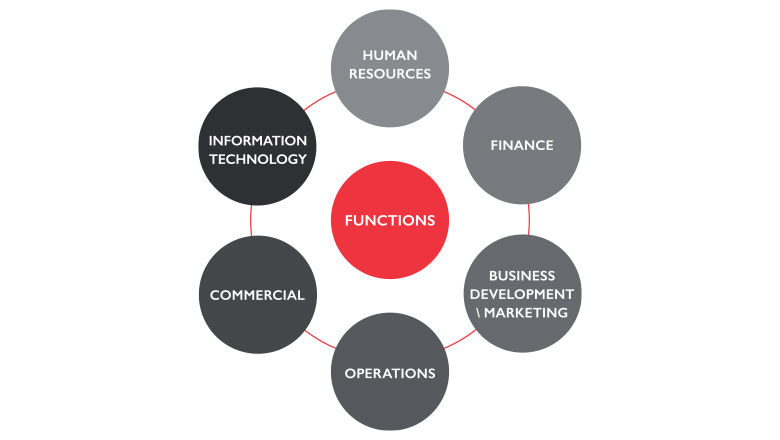
Business Functions
Businesses must concentrate on a few essential tasks in order to run efficiently:
Marketing
Marketing through branding, social media, and advertising, assists companies in connecting with their target audience. The proper message will always reach the right audience thanks to effective marketing.
Operations
Operations production, quality assurance, and logistics are just a few of the daily tasks that make up operations in a business.
Finance
Money management is an essential corporate task. Finance makes ensuring that a business can grow sustainably and stays solvent, from investment to budgeting.
Human Resources
Humans are the heart and soul of any business. Human resources oversee hiring, onboarding, training, welfare of workers, and adherence to labour regulations.
Key Elements of a Successful Business
A company needs some fundamental components to be in place in order to grow and succeed over the long run. These essential components offer the organisation, concentration, and flexibility required to expand in a cutthroat market.
Vision and Mission
The vision and mission of an organisation are essential to its identity. The company’s long-term aspirational goals and future state are represented in the vision. It acts as a compass, assisting the organisation in staying on course as the market shifts. In contrast, the mission is more concerned with the here and now. It outlines the goal of the company, the benefits it offers to clients, and the ways it plans to reach out to the market.
Employee motivation, stakeholder alignment, and customer understanding of the company’s basic values are all facilitated by clear vision and mission statements. In order to ensure that everyone in the team is working towards the same objective, successful organisations frequently convey their vision and mission clearly.
Strategy
The plans and strategies a company uses to beat its rivals and accomplish its goals are referred to as business strategies. It entails seeing market opportunities, figuring out what customers need, and efficiently allocating internal resources to take advantage of those chances. Depending on the nature of the organisation, the state of the market, and its objectives, several strategies are used.
For instance, some companies might pursue differentiation by providing distinctive goods or services, while others might take a cost-leadership approach, emphasising being the least expensive choice. Sustaining growth, staying ahead of the competition, and handling market swings all depend on having a clearly defined plan.
Customer Focus
Probably one of the most important elements of a successful enterprise is a customer-focused approach. It entails centring all choices and actions around the needs of the client. Knowing its consumers’ wants, needs, and areas of pain enables a company to develop goods and services that actually address issues, resulting in happy and devoted customers.
Beyond just selling goods, customer-centric companies aim to deliver great experiences at every point of contact. This could involve attentive customer service, tailored offerings, and ongoing development informed by user input. Companies that put the needs of their customers first in today’s fiercely competitive market frequently reap the benefits of increased brand loyalty, favourable word-of-mouth, and repeat business.
Innovation and Adaptability
Innovation and adaptation are essential to staying relevant and successful in the ever-changing corporate world. Innovation is the introduction of novel concepts, procedures, or goods that increase productivity, satisfy changing consumer needs, or address new issues. It can take the form of ground-breaking technical breakthroughs or little, gradual modifications.
An organisation’s capacity to react swiftly to outside influences, such as changes in the market, shifts in the economy, or the emergence of disruptive technology, is referred to as adaptability. Slow-moving enterprises run the risk of becoming out of style. For instance, in order to remain competitive, the emergence of digital technology has compelled many established organisations to embrace e-commerce platforms or implement new marketing techniques.
Importance of Business Planning
Planning a business strategy is essential to any successful venture. It guarantees that every choice aligns with the overall plan and offers a clear roadmap for accomplishing both short- and long-term goals.
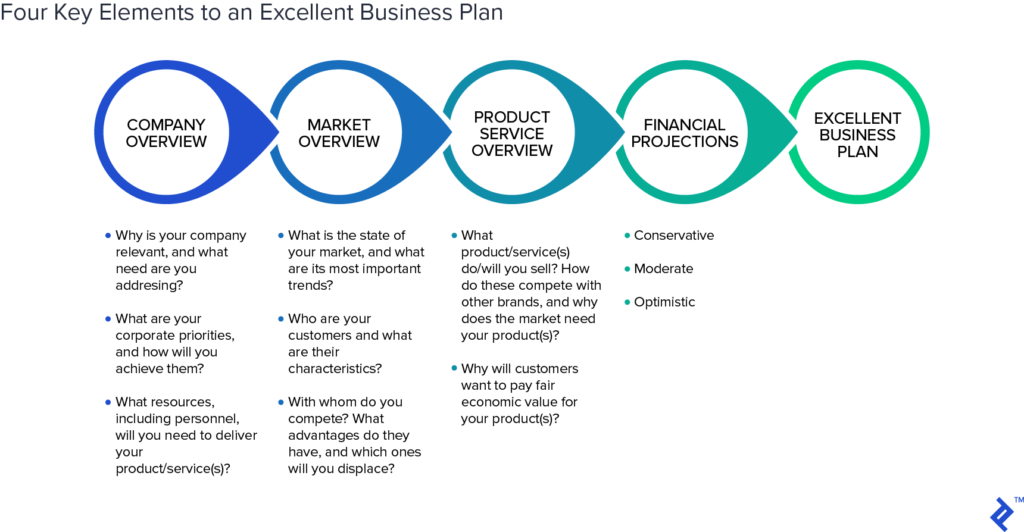
Business Plan Overview
A written document that describes the objectives, tactics, market analysis, and financial projections of a venture is called a business plan. It functions as a communication tool and a strategy guide for all parties involved, such as partners, employees, and investors. A well-written plan specifies the target market, describes the competitive environment, and lists the operational procedures required for success.
It also acts as a growth roadmap, offering quantifiable standards that can be used to monitor advancement and modify plans of action as necessary. Since a plan shows the venture’s profitability and viability, it is often necessary for entrepreneurs to obtain funding.
Strategic Objectives
The long-term aims that drive an organization’s success are known as strategic goals. These are high-level results that give guidance for daily operations and are consistent with the company’s vision and mission. A strategic objective can be to launch a new product line, enter new markets, or raise market share by a specific percentage.
Establishing measurable, clear goals enables firms to concentrate their resources on the most important tasks. Additionally, it keeps teams engaged and in sync by ensuring that everyone is working toward the same goal. As an organization develops or market conditions change, strategic goals are usually reviewed and modified.
Risk Management
All enterprises have risks, whether they stem from operational difficulties, financial uncertainty, or outside market pressures. Identifying possible risks to the organization, analyzing their impact and likelihood, and creating mitigation plans are all part of risk management.
Organizations might, for example, control financial risk by maintaining a varied clientele, ensuring they have sufficient cash on hand, or obtaining insurance. By implementing quality control procedures, providing personnel training, or making technological investments, operational risks can be reduced. Legal and regulatory risks can be managed by staying abreast of legal developments and implementing compliance strategies. Organizations that practice proactive risk management are better equipped to handle unexpected events and overcome obstacles with minimal disruption.
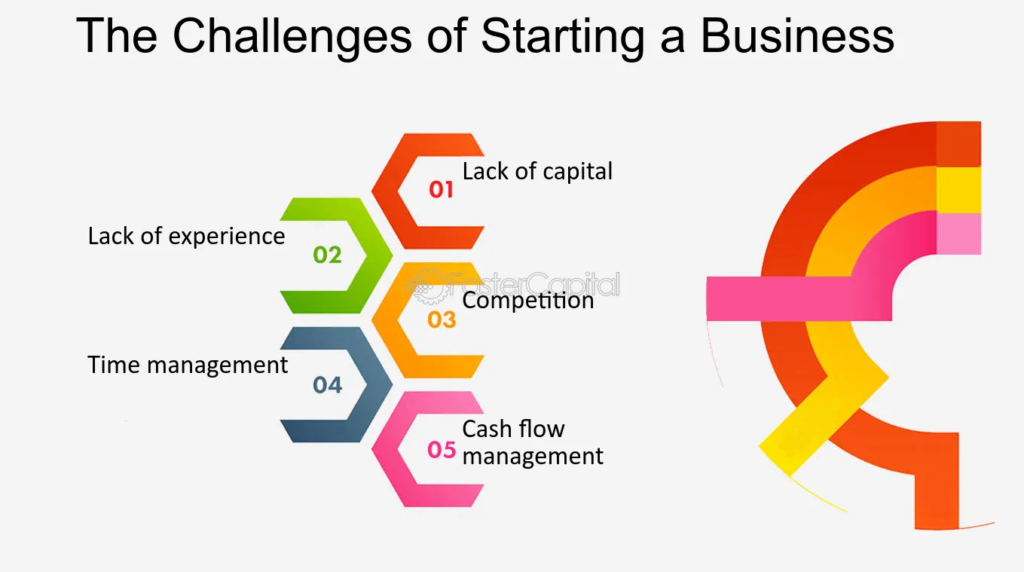
Challenges in Running a Business
There are many obstacles to overcome when launching and operating a business. Any entrepreneur or business leader’s adaptability and resilience may be put to the test by these obstacles.
Competition
One of the most enduring obstacles in business is competition. To gain market share, companies need to set themselves apart in almost every industry. Companies must constantly innovate and improve their goods since rivals might provide more inventive items, better customer service, or lower rates.
Businesses need to perform in-depth market research, closely monitor industry trends, and continuously look for ways to improve if they want to stay ahead of the competition. A few tactics companies can use to stay competitive are developing a strong brand, encouraging client loyalty, and keeping operations running smoothly.
Market Changes
The industry is always evolving due to many variables such evolving customer preferences, developments in technology, and variations in the economy. For example, the emergence of e-commerce has fundamentally changed the retail environment, requiring the adaptation of established brick-and-mortar companies to avoid losing market share.
Companies are better positioned to take advantage of new opportunities and stay ahead of the competition when they identify and adapt to changes in the market. This frequently calls for flexibility in judgement and the capacity to change business plans as needed.
Cash Flow Management
Any business’s lifeblood is its cash flow. Financial difficulties can arise even for prosperous organisations if there is insufficient cash flow. Making sure the business has enough money on hand to pay bills, pay staff, and make growth-oriented investments is all part of managing cash flow.
Ineffective cash flow management might result in lost opportunities, trouble making supplier payments, or even collapse. Maintaining a sound balance between incoming and outgoing funds, careful planning, and precise financial forecasts are all necessary for effective cash flow management.
Regulatory and Legal Hurdles
Companies have to manage a complicated web of legal requirements, including labour laws, taxes, and industry-specific guidelines. Although following to these rules can be expensive and time-consuming, doing otherwise may result in penalties, legal action, and reputational harm for the business.
Avoiding regulatory traps requires investing in legal competence and being up to date on changes to the law. Many companies make sure they conform with all legal obligations by hiring compliance officers or consulting with legal professionals.
Global Impact of Business
Businesses have an impact on the world at large that goes beyond their local marketplaces in today’s connected world. Companies’ operations and interactions with the outside world are changing as a result of globalisation, technology, and sustainability.
Globalization and International Trade
The process of globalisation has created new avenues for enterprises to grow internationally. Businesses can enter new markets through international trade, take advantage of global supply networks, and boost sales by offering goods and services to a wider customer base.
But going global also means facing obstacles like managing currency swings, comprehending cultural differences, and negotiating foreign legislation. Companies that are successful in the global market frequently have a thorough awareness of international business procedures and are able to modify their plans according to the needs of various geographic areas.
Technology and Digital Transformation
The way businesses run has been significantly impacted by the development of technology. Digital tools have made it possible for organisations to run more efficiently, contact customers in new ways, and make data-driven decisions. These tools range from automation to data analytics to artificial intelligence (AI).
E-commerce platforms, for instance, have made it possible for companies to sell goods online and reach a worldwide customer base at a low cost of overhead. In the meantime, cloud computing has improved flexibility and cut costs for businesses by enabling them to operate apps and store data remotely. Businesses that want to remain competitive in the modern market require digital transformation.
Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Businesses are facing more and more pressure to implement ethical and sustainable practices as public awareness of environmental and social issues rises. Customers are calling for increased openness, and they are more likely to support companies that place a high priority on social responsibility and sustainability.
Reducing carbon footprints, using fair trade, and obtaining resources ethically are some examples of sustainable activities. Companies who ignore these issues risk consumer backlash, which could harm their brand’s reputation and cause them to lose market share.
The Future of Business
Rapid technological breakthroughs, the emergence of startups, and shifting customer behaviour are shaping the face of business.
Emerging Trends
Artificial Intelligence (AI), automation, and remote labour are examples of technological innovations that are completely changing how businesses operate. AI-powered solutions help businesses run more smoothly and make better decisions by automating laborious operations, analysing massive volumes of data, and even predicting client preferences.
The workforce is changing as a result of automation, with machines taking over many ordinary jobs. In the meantime, conventional office settings are changing due to the COVID-19 pandemic’s acceleration of the increase of remote labour. Enterprises that adopt these patterns and modify their activities accordingly have a greater chance of succeeding in the long run.
Startups and Entrepreneurship
With their innovative business strategies and disruptive technologies, startups are spearheading innovation. Rapid solutions that meet the requirements of changing consumers and tackle global concerns are being developed by entrepreneurs.
Evolving Consumer Behaviors
Consumers of today want companies that share their ethical and environmental values and demand convenient, personalised experiences. To live up to these expectations, businesses need to modify their marketing plans and implement sustainable practices.
Conclusion
In order to shape economies and improve societal well-being, business is essential. Profits are important, but so are meeting consumer demands, creating jobs, and promoting community development. Businesses, no matter how big or little, sustain supply networks, stimulate trade, and power industries. A clear vision, flexibility in the face of change, and a solid grasp of operations, finance, marketing, and customer relations are all necessary for success.
Globalisation, artificial intelligence, and digital transformation are all driving changes in the business landscape. Businesses that prioritise social responsibility and sustainability have a greater chance of establishing enduring bonds with ethical customers. Success in the competitive world of today demands resilience, adaptability, and a dedication to constant growth. Those that don’t lose out on innovation and strategic planning will prosper, converting obstacles into chances and leaving a lasting impression.
Thanks for reading.