Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Importance of Developing a Winning Business Model
- What is a Business Model?
- Definition and Key Components
- Step 1: Identify Your Value Proposition
- Examples of Value Propositions
- Step 2: Identify Target Customers
- Understanding Your Ideal Customers
- Important Questions to Pose
- Step 3: Determine Your Revenue Model
- Common Revenue Models
- Importance of Diverse Income Sources
- Step 4: Define Your Cost Structure
- Understanding Fixed and Variable Costs
- Step 5: Develop a Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Key Components of a Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Step 6: Build Key Partnerships
- Importance of Strategic Alliances
- Examples of Key Partnerships
- Step 7: Plan for Scalability
- Aspects of Scalability
- Managing Growth and Demand
- Step 8: Track and Optimize Performance
- Key Metrics to Monitor
- Conclusion: Creating a Sustainable and Profitable Business Model
- Importance of Flexibility and Value Creation
- Additional Resources
- Link to Related Articles
One of the most crucial steps in starting and expanding any business is developing a winning business model. Whether you’re the creator of a startup or the manager of an existing firm, a well-crafted business model serves as a guide for how your enterprise runs, makes money, and expands over time. This blog will guide you through the process of developing a successful business model and offer insights into important elements such as target market, income sources, value proposition, and scalability. A strong business model is key to long-term success and adaptability in a competitive market.
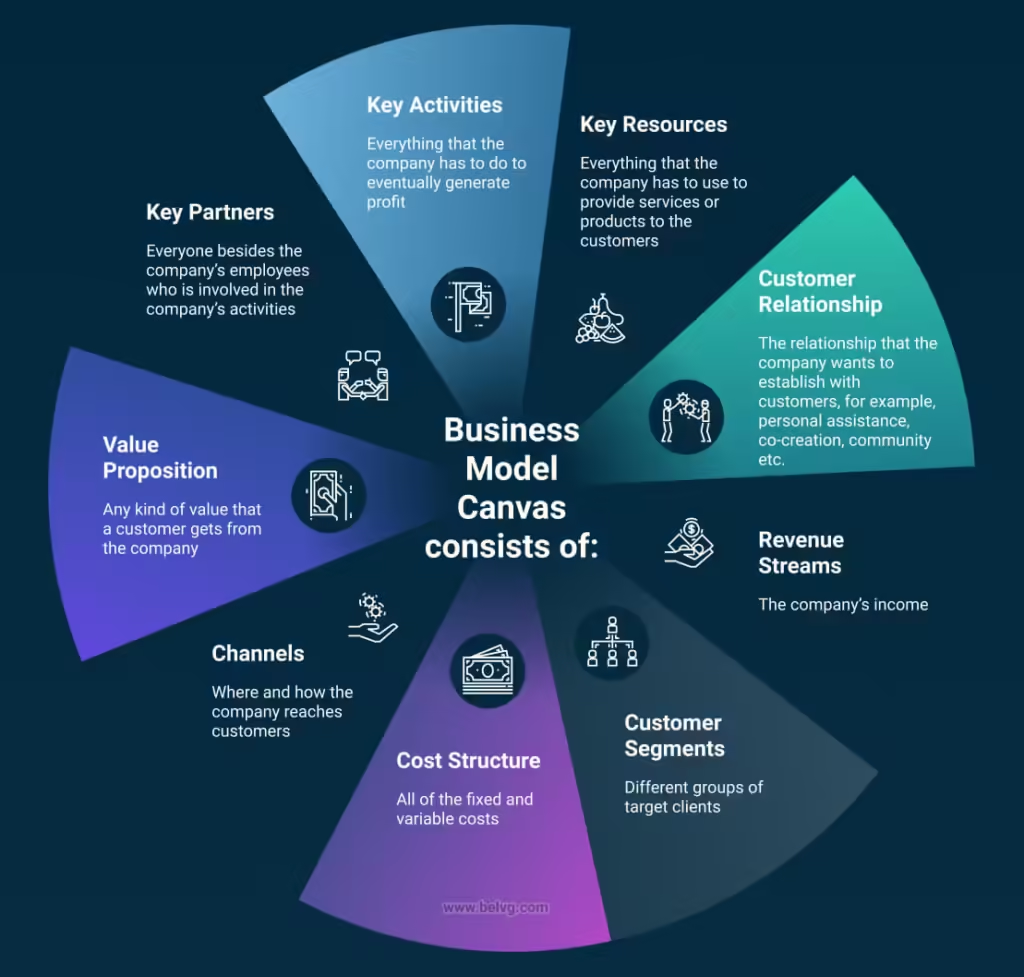
What is a Business Model?
A business model is a comprehensive plan that describes how an organisation will bring in money and turn a profit from its activities. It contains details on the goods and services a company provides, who its target market is, what makes them stand out from the competition, and how you intend to approach and serve to them.
At its core, a business model answers critical questions:
- What value will your company deliver?
- Who are your customers?
- How will you earn revenue?
A Business Model provides the framework for decision-making and sets the foundation for operational, marketing, and financial strategies.
Step 1: Identify Your Value Proposition
The process of developing a winning company model begins with defining your value proposition. This basically sums up what sets your product or service apart and explains why buyers would pick you over rivals.
Examples of Value Propositions:
- Cost efficiency: Offering a product or service at a lower cost than the competition.
- Innovation: Providing a new or better solution to a problem.
- Convenience: Making the customer experience faster or easier.
- Customization: Tailoring the product to fit specific customer needs.
Your value proposition should address a customer’s issue or need and make it clear what advantages using your good or service will bring to them.
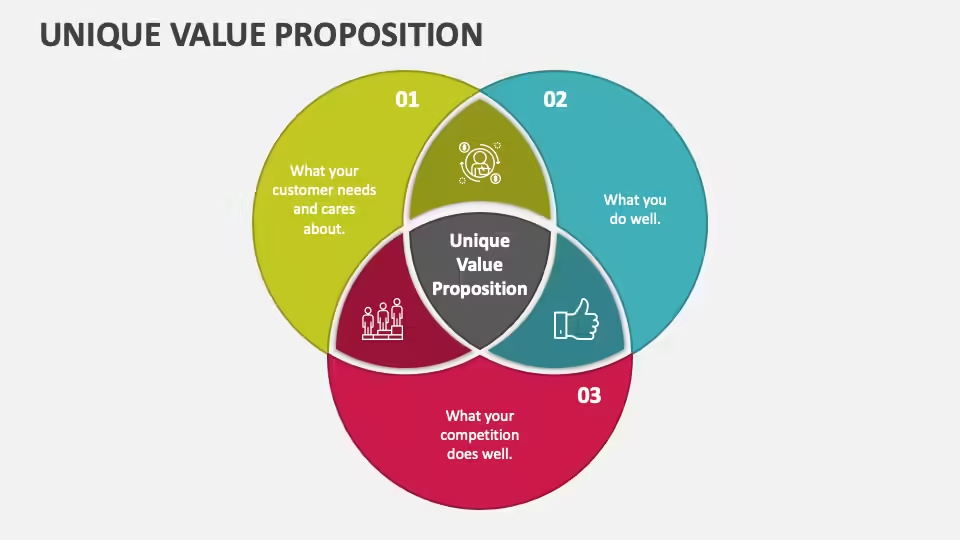
Step 2: Identify Target Customers
Developing a company strategy requires having a thorough understanding of your target market. You may effectively adjust your products, services, and marketing to match the needs of your ideal customers by being aware of who they are.
Important Questions to Pose:
- Who are the perfect clients for you? (Location, demographics, etc.)
- What issues do they have?
- How can your offering address these issues?
- How are you going to contact them?
Divide your audience into groups based on shared attributes (such as age, income, or occupation) to develop a more customised strategy. To help direct marketing and product development efforts, think about creating fictionalised versions of your ideal consumers, or buyer personas.
Step 3: Determine Your Revenue Model
Our company will make money according to its revenue model. The best revenue model for your business will rely on a number of factors, including your industry, line of business, and state of the market.
Here are some common Revenue Models:
- Direct Sales: Selling your product or service directly to customers.
- Subscription Model: Charging customers a recurring fee (monthly, yearly) for access to your service.
- Freemium: Offering a basic version of your product for free, but charging for premium features.
- Advertising: Earning revenue by selling ad space on your platform.
- Licensing: Charging other companies to use your intellectual property, patents, or software.
Having several sources of income helps strengthen the financial stability of your company. Make sure to specify the price you will charge for your good or service as well as how it will compare to that of your rivals.
Step 4: Define Your Cost Structure
KKnowing your expenses is essential to your company’s long-term viability. How much cash you need to launch and run your firm, as well as how you want to handle costs over time, will all depend on your cost structure.
Types of Costs:
- Fixed Costs: Expenses that remain constant, such as rent, salaries, and utilities.
- Variable Costs: Expenses that fluctuate depending on production levels, such as raw materials and shipping costs.
To maintain profitability, you must strike a balance between your sources of income and expenses. A good business strategy should be scalable, which means that when the number of customers expands, your earnings should rise while maintaining control over operating expenses.

Step 5: Develop a Marketing and Sales Strategy
Developing a plan for reaching your audience and turning them into paying customers comes after you Have your value proposition, target market, and revenue model. This involves selecting the appropriate ways and strategies to advertise your good or service.
Key Components of a Marketing and Sales Strategy:
- Channel Strategy: Decide which marketing channels you will use to reach customers (e.g., social media, email marketing, paid ads).
- Sales Funnel: Develop a sales process that moves potential customers through stages, from awareness to purchase.
- Customer Retention: Once a customer buys from you, how will you keep them engaged and coming back? Consider loyalty programs or email marketing for long-term engagement.
A strong marketing plan will draw in leads, raise brand awareness, and eventually boost conversions. Make sure that the behaviours and preferences of your target audience are reflected in your marketing efforts.
Step 6: Build Key Partnerships
FForming strategic alliances can improve operations, increase market penetration, or even save expenses for a lot of businesses. Consider how you may work with other companies or organisations that share the same objectives as your own.
Examples of Key Partnerships:
- Suppliers: Reliable suppliers who provide the materials or products you need.
- Distributors: Companies that help you distribute your product to a broader audience.
- Technology Partners: Businesses that offer technological support to improve operations.
Establishing strong partnerships can be a competitive advantage, providing you with resources and capabilities that you don’t have in-house.
Step 7: Plan for Scalability
A scalable business plan is one that can expand without experiencing associated rises in expenses. This is especially crucial in sectors like technology, where network effects and automation allow companies to grow quickly.
Aspects of Scalability:
- Is it possible to easily extend or duplicate your offering without incurring major additional costs?
- Exist chances to diversify into other product categories or markets?
- When your firm expands, how will you handle the additional demand from customers?
Scalability guarantees long-term profitability and sustainability by enabling a company to expand rapidly while keeping costs under control.
Step 8: Track and Optimize Performance
Ultimately, it’s crucial to monitor important metrics and optimise for performance once your company plan is in place. To find opportunities for improvement, examine financial information, customer reviews, and other performance indicators on a regular basis.
Metrics to Track:
- Revenue Growth: Are your revenue streams increasing month over month?
- Customer Acquisition Cost: How much does it cost to acquire a new customer?
- Churn Rate: How many customers are you losing over time, and why?
- Net Profit Margin: Are you profitable after covering all your costs?
By regularly reviewing these metrics, you can make informed decisions about your business model, ensuring its long-term success.
Conclusion: Creating a Sustainable and Profitable Business Model
The method of creating a business model is not universally applicable. It requires an in-depth knowledge of your clients, market, and business trends. You can develop a business model that is flexible and scalable in the long run, in addition to being successful in the near term, by following the instructions provided in this tutorial.
Recall that a profitable business model involves more than just generating revenue. It all comes down to providing value to your clients, running your company profitably, and setting yourself up for future expansion. A well-structured business model is key to achieving sustainable growth.
StartUp
Creating a strong business model is one of the most important aspects of any startup‘s success. Your business model, as a startup founder, is the blueprint that outlines how you plan to add value for consumers, make money, and expand your business over time. A well-thought-out plan is essential to winning over investors and guaranteeing long-term survival in the cutthroat world of startups.
Startups frequently face particular challenges like limited funds, changing markets, and the requirement to make swift adjustments. To handle these rapid changes, a startup’s strategy needs to be both flexible and adaptive. For instance, a startup may decide to start with a freemium approach to attract users, then, as that user base expands, switch to a subscription-based model. Understanding these dynamics is imperative for your startup to establish a scalable and viable framework.
Partnerships can also be extremely important to a startup’s success. Collaborating with other companies can help a startup grow more quickly and save operating expenses, whether it’s for distribution channels or technology support. These alliances can give young businesses a competitive advantage by providing access to resources and skills they may not yet have in-house.
Here’s your go-to guide for everything you need to know about Business.
https://blogs.devartverse.io/category/business
Thanks for Reading.