Table of Contents
- AI vs Design: Introduction
- AI in Design: Revolutionizing Creativity
- The Role of AI in Modern Graphic Design
- Human Creativity vs. AI-Generated Designs
- AI vs Design: Ethical Concerns
- Opportunities for Collaboration: Designers Shaping AI
- Practical Applications of AI vs Design
- AI’s Limitations in Graphic Design
- The Future of AI vs Design
- Conclusion
AI vs Design: Absolutely, the development of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed many sectors, including graphic design. AI is establishing itself as an interesting, if controversial, complement to the creative process thanks to its powers to analyse, learn, and create. Others worry that AI might replace human creativity, while others see technology as an important ally for designers. This blog explores the complex relationship between AI and graphic design, providing a fair assessment of the advantages and disadvantages of this ground-breaking technology.
AI in Design: Revolutionizing Creativity
AI vs design is becoming a reality that is influencing how professionals approach their work, not just a futuristic idea. Algorithms may create ideas, streamline workflows, and even build complete designs, as shown by AI-powered applications like Adobe Sensei, Canva, and DALL·E 2.
AI vs design is evident when AI tools suggest colour schemes and layouts or automate hard jobs, showcasing their immense utility. However, the question remains whether AI can genuinely replicate the creative spark that defines human artwork. AI vs design continues to be a compelling discussion as technology advances, blending innovation with artistry.

The Role of AI in Modern Graphic Design
AI has a wide range of applications in graphic design, from ideation to finished product. Let’s examine its contributions in more detail:
Automating Routine Activities:
Tasks like resizing photos, changing layouts, or eliminating backgrounds sometimes take hours for designers. AI completes these jobs quickly, freeing up time for more innovative and strategic pursuits.
Coming Up with Design Concepts:
Artificial intelligence (AI) tools can identify patterns and suggest design concepts suited to particular sectors or topics. This may encourage designers to experiment with unusual mixes and styles.
Increasing Cooperation:
AI elements are integrated into platforms such as Figma, which facilitate smooth team collaboration by providing real-time suggestions and adjustments.
Large-Scale Personalisation:
Designers may now produce tailored content for a variety of audiences thanks to AI. E-commerce companies, for instance, employ AI to create advertisements that are customised to each user’s tastes.
Human Creativity vs. AI-Generated Designs
The debate between human creativity and AI-generated designs centers on originality, emotional depth, and cultural relevance. While AI excels in efficiency and data-driven insights, it often lacks the nuanced understanding that human designers bring to the table.
The Human Advantage
Emotional Connection: Human designers intimately connect with audiences by incorporating their own feelings and experiences into their work.
Cultural Sensitivity: Because humans are better at understanding cultural settings than AI, designs are inclusive and suitable.
Storytelling: Designers create images with captivating narratives that are difficult for AI to accurately reproduce.
The Benefits of AI
Speed and Scalability: AI generates solutions at a scale that is impossible for humans to achieve by processing huge amounts of data rapidly.
Data-Driven Decisions: AI improves efficacy by using analytics to guide design decisions.
| Aspect | AI Design | Human Design |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Generates designs quickly, often in seconds. | Takes more time due to creative thinking and manual effort. |
| Creativity | Limited to patterns and styles learned from data; lacks emotional depth. | Highly creative, incorporating emotions, cultural nuances, and unique perspectives. |
| Customization | Can adapt to given inputs but may struggle with deep personalization. | Fully customizable to specific client needs with a personal touch. |
| Consistency | Ensures uniformity across large-scale projects. | May require additional effort to maintain consistency in large projects. |
| Understanding Context | Relies on programmed algorithms and lacks deeper contextual understanding. | Can understand complex cultural, emotional, and market-specific contexts. |
| Cost | Typically more cost-effective for repetitive or simple tasks. | Can be expensive due to expertise and time involved. |
| Complexity Handling | Excels in repetitive, data-driven designs or automation. | Better suited for complex, abstract, or highly creative projects. |
| Innovation | Limited to recombining existing data and trends. | Capable of groundbreaking innovation and out-of-the-box ideas. |
| Emotional Connection | Cannot inherently create emotionally resonant designs. | Designs can evoke strong emotions and connections with the target audience. |
| Adaptability | Restricted to predefined algorithms and updates. | Easily adapts to new challenges, trends, and feedback. |
| Collaboration | Operates as a tool with limited collaborative capabilities. | Thrives in collaborative environments, incorporating feedback and teamwork. |
| Ethics and Values | Cannot independently consider ethical implications; depends on user input. | Can incorporate ethical considerations and personal or brand values into design decisions. |
AI vs Design: Ethical Concerns
While AI offers incredible potential, it also raises significant ethical issues that the design community must address:
- Plagiarism and Originality
AI frequently uses previously published work, making it difficult to tell the difference between originality and plagiarism. Designers need to consider whether content produced by AI violates intellectual property rights. - Algorithm Bias
AI models that are trained on biassed datasets have the potential to reinforce views and produce designs that are not inclusive or diverse. - Security of Data and Privacy
Access to user data is necessary for using AI, which raises questions about how this data is handled and preserved. Designers are responsible for making sure privacy laws are followed. - Accountability
When an AI tool produces an offensive or flawed design, determining accountability can be challenging. Should the blame lie with the tool, its developers, or the designer using it?

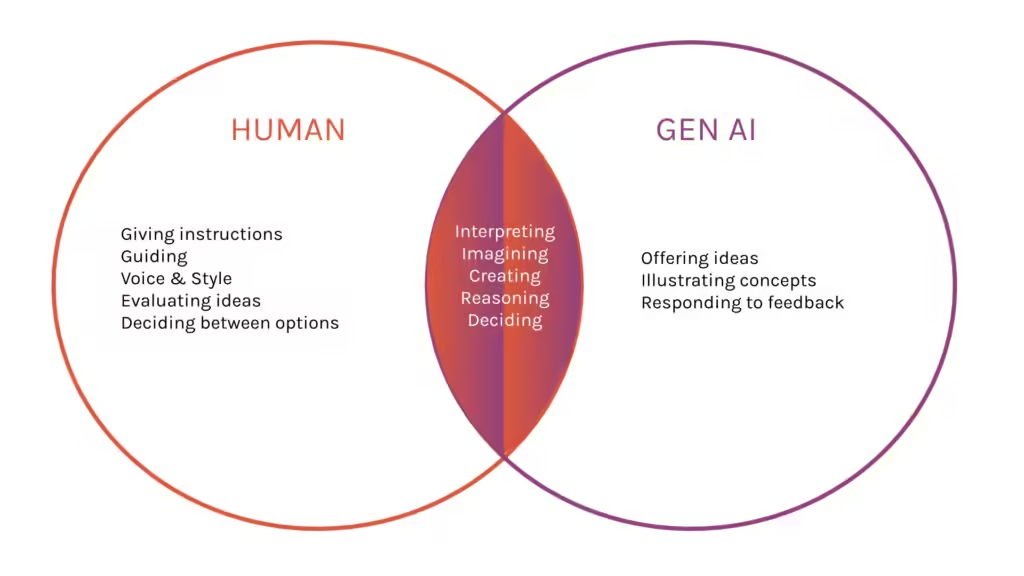
Opportunities for Collaboration: Designers Shaping AI
Rather than viewing AI as a competitor, designers can collaborate with it to push the boundaries of creativity.
1. Designing AI Tools:
Graphic designers play a crucial role in developing intuitive interfaces for AI tools, ensuring they cater to user needs.
2. Training AI Models:
Designers provide valuable feedback to refine AI algorithms, improving their ability to produce relevant and accurate outputs.
3. Defining Ethical Standards:
By establishing guidelines for AI use, designers can ensure ethical practices in the industry.
4. Combining Human Intuition with AI Efficiency:
The future of design lies in blending human intuition with AI’s analytical power. This synergy can lead to groundbreaking innovations.
Practical Applications of AI vs Design
AI tools are increasingly essential in a number of graphic design domains, such as:
- Image editing: AI is used by programs like Luminar Neo to improve images, change lighting, and eliminate flaws.
- AI makes typographic recommendations that complement the concept of a project.
- Layout Optimisation: AI-generated layouts preserve professional standards while saving time.
- Data Visualisation: Making detailed infographics is made easier by programs like Tableau.
AI’s Limitations in Graphic Design
Despite its potential, AI is lacking in certain areas that call for:
- Abstract Thinking: AI finds it difficult to understand and creatively apply abstract ideas.
- Emotional Depth: The emotional resonance of human-designed graphics cannot be replicated by it.
- Cultural Contexts: In international design projects, AI frequently fails to pick up on minor cultural cues.
The Future of AI vs Design
AI vs Design: As AI advances, it will become stronger in visual design. However, it is unlikely to fully replace human designers. Instead, AI will be a powerful tool that boosts human creativity and enables designers to complete more tasks faster.
AI vs Design shows that by accepting AI and seeing technology as a tool for innovation rather than a threat, designers can maintain their lead in a rapidly changing sector.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the debate between AI vs Design is not about competition but collaboration. AI vs design has the potential to revolutionize the industry, but the human touch remains irreplaceable. As designers harness the power of AI responsibly, the future promises a harmonious blend of technology and creativity, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the world of design.
Here’s your go-to guide for everything you need to know about Design
https://blogs.devartverse.io/category/graphics-designing/
More for other blogs that are valuable to know.
Thanks for Reading.