From being a science fiction idea to being a necessary component of our everyday existence, artificial intelligence (AI) has come a long way. Artificial intelligence is transforming industries and altering how we interact with the world around us, from self-driving cars to intelligent virtual assistants. But as AI becomes more prevalent, solid leadership and moral regulation become more important. We will look at the background of AI, the worldwide approach to AI regulation, and significant advancements in AI services and technologies in this blog.
A Brief History of AI: From Ancient Myths to Modern Marvels
The idea of developing artificial intelligence has its roots in the past. Greek mythology depict Hephaestus, the god of workmanship, creating creatures like robots, and ancient Egyptians created moving artwork with complex internal gears. However, in the early 19th and 20th century, the groundwork for artificial intelligence as we know it started to take shape.
The Analytical Engine, created in 1836 by mathematician Charles Babbage and Ada Lovelace, was the first example of a programmable machine. Lovelace, who recognised that machines could do jobs involving algorithms and go beyond simple computations, is sometimes regarded as the pioneer of computer programming. The foundation of modern computing was set by British mathematician Alan Turing in the 1930s with his introduction of the idea of a universal computer that could imitate any other machine.
Key Milestones in AI Development:
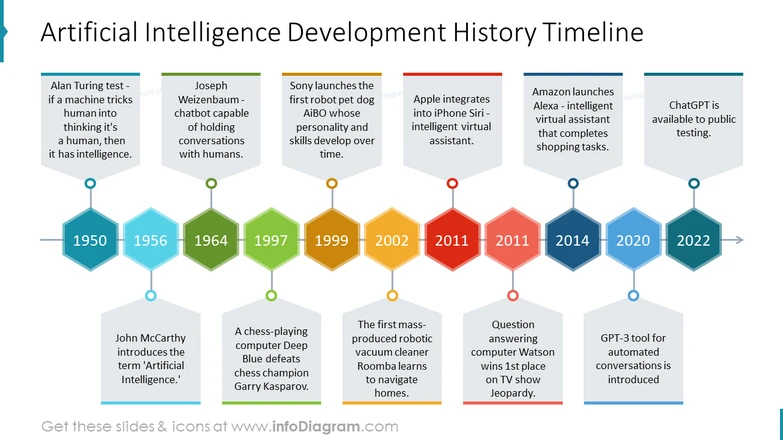
- 1950s: Alan Turing developed the “Turing Test,” a method for figuring out whether a machine is intelligent enough to mimic a person. In the meantime, the science of artificial intelligence officially began in 1956 when John McCarthy used the term “artificial intelligence” at a conference at Dartmouth College.
- 1960s–1970s: Despite encouraging developments, including the development of pioneering natural language processing (NLP) systems like ELIZA, artificial intelligence (AI) experienced obstacles because of limited processing capacity, which led to the first “AI winter.”
- 1980s–1990s: Expert systems and deep learning saw a rebirth in AI research, but this was followed immediately by the second AI winter. Developments in big data, computing power, and machine learning by the mid-1990s gave the area a fresh start. The 1997 victory of IBM’s Deep Blue over chess champion Garry Kasparov was a significant turning point.
- 2000: Advancements in natural language processing, image recognition, and recommendation engines were made during this time, as seen by the search engines on Google, Facebook, and Amazon.
- 2010s and Later: With breakthroughs like Apple’s Siri, self-driving cars, and the introduction of OpenAI‘s GPT models, the field of artificial intelligence had a boom that culminated in the 2022 release of ChatGPT.
The European Union’s Proactive Approach to AI Regulation
As AI technology develops, governments throughout the world are trying to figure out how to control its application and advancement. The European Union (EU) has established one of the most extensive regulatory structures for AI in the world in recent years, marking a significant advancement in AI regulation.
The EU’s AI Act: Pioneering AI Governance
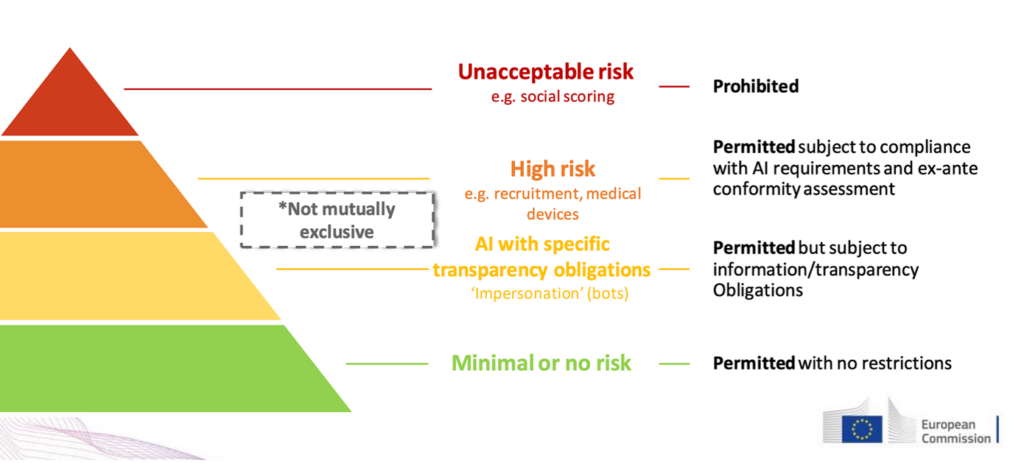
The European Union’s AI Act, which was adopted by the Council, establishes different regulatory thresholds according to how dangerous AI systems are. Applications of AI in vital fields including infrastructure, healthcare, and biometrics are closely monitored. The greatest dangers to privacy, security, and ethics are minimised while AI innovation is promoted thanks to this risk-based strategy.
Furthermore, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which places strict restrictions on how businesses can handle customer data, has played a significant role in regulating AI. This affects the training and functionality of AI systems, particularly those that interact with consumers. The AI Act is anticipated to have a comparable impact on AI governance globally.
The U.S. Approach to AI Governance: Slow but Steady Progress
The US has not yet implemented extensive federal AI legislation, in contrast to the EU. Nonetheless, deliberate efforts and executive acts are advancing the situation. President Biden, for instance, issued an executive order in October 2023 requiring federal agencies to evaluate and handle AI issues. Furthermore, in 2022, the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy released the “Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights,” which offered companies recommendations for implementing AI in an ethical manner.
In spite of these attempts, state-level initiatives have taken the lead because there isn’t a single federal strategy. The significance of AI legislation that strike a balance between innovation, competitiveness, and risk management has also been underlined by the US Chamber of Commerce. The EU’s stricter restrictions may have a knock-on effect on U.S. policy, just like the GDPR did for global data privacy standards.

The Challenges of Regulating AI: A Complex and Rapidly Evolving Field
The diversity and rapid evolution of AI create a unique challenge for the creation of effective legislation. These are a few of the main concerns:
AI’s Broad Applications: AI encompasses technologies ranging from NLP and image recognition to autonomous systems. Each of these areas has different risks and opportunities, making it difficult to draft universal regulations.
Ethics and Accountability: AI systems often operate in opaque ways, with developers and users unable to fully understand how algorithms arrive at their conclusions. This “black box” nature complicates accountability and governance.
The Speed of Innovation: The fast pace of AI advancements often outstrips regulatory frameworks. Breakthroughs such as ChatGPT and DALL-E can render existing laws obsolete in a short period.
Preventing Malicious Use: While laws may deter legitimate companies from misusing AI, they are less likely to prevent malicious actors from exploiting AI for harmful purposes.
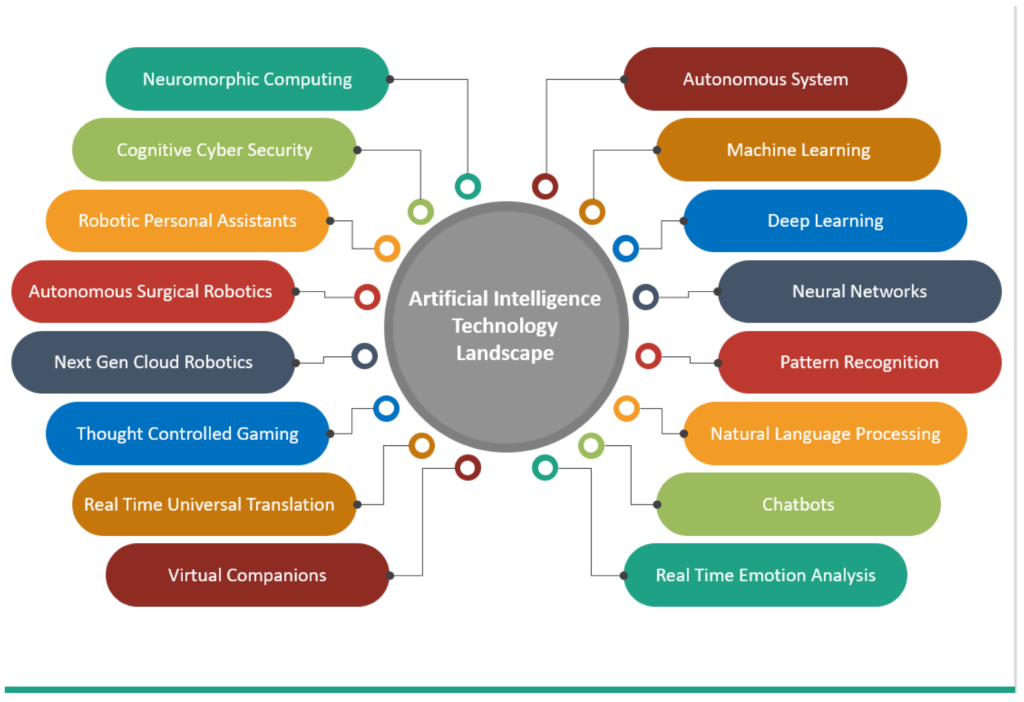
AI Tools and Services: Key Innovations and Ecosystem Growth
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) services and products has been fueled by the mutually beneficial link between hardware and AI algorithms. Advances in deep learning, neural networks, and the hardware needed to handle large volumes of data have been crucial to the development of artificial intelligence since the early 2000s.
Transformers: A New Chapter in NLP
Google conducted ground-breaking research on transformers for their 2017 publication “Attention Is All You Need.” Transformers enhance artificial intelligence (AI) model performance in a variety of tasks, including translation, text production, and summarisation, by utilizing self-attention techniques.
Transformers using Generative Pre-training (GPTs)
Artificial intelligence (AI) has transformed how both individuals and enterprises employ Generative Pre-Trained Transformers (GPTs), including OpenAI’s GPT series. Because these models have already undergone extensive training on a large volume of data, they can be more cheaply and expertly adjusted for particular uses. GPT models have greatly reduced the obstacles to artificial intelligence (AI) adoption, allowing companies of all sizes to take advantage of state-of-the-art artificial intelligence (AI).
AI Cloud Services: Opening Up AI for All
Major cloud service providers, such as Amazon AI, Microsoft Azure AI, and Google Cloud AI, have been instrumental in enabling businesses to use artificial intelligence (AI). These services allow enterprises to incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities into their operations without requiring a thorough understanding of machine learning or data science.
Conclusion: The Future of AI is Both Promising and Complex
AI promises to revolutionise everything from healthcare to transforming industries through intelligent systems and automation. But just as AI technology advances, so too must the legal systems that oversee it. A worldwide conversation on responsible AI innovation is facilitated by the EU‘s aggressive stance and the United States‘ expanding activities. At the same time, developments in AI services and tools are expanding access to AI and increasing its scalability and affordability for enterprises globally.
Maintaining an ethical, responsible development process while promoting innovation will be crucial for navigating the AI future. Keeping up with technology developments and legal changes will be crucial for organisations wishing to implement AI if they want to maximise its promise and minimise its hazards..
The Future of AI: Navigating the Promising Yet Complex Landscape
It is critical that we understand both the new problems and the opportunities that AI brings as we continue to push the limits of what technology can accomplish. While AI has great promise for the future, its social ramifications must be carefully considered.
AI and Human Coordination: Boosting Potential
AI is being utilised more and more to supplement human abilities rather than to replace them. Artificial intelligence (AI) is enhancing human abilities in domains like healthcare, education, and the creative arts, opening up new avenues for cooperation.
Healthcare: Transitioning from Diagnostics to Customised Treatment
AI-driven technologies are transforming healthcare through improving the precision of diagnoses and customising therapies. AI systems, for example, are highly accurate at analysing medical images, which helps doctors find errors early. AI is used in personalised medicine to help customise therapies based on each patient’s unique genetic profile, improving results and minimising negative effects.
Education: Virtual Classrooms and Adaptive Learning
AI is enabling adaptable learning environments in education that are customised for the demands of each individual student. While artificial intelligence-powered virtual classrooms can provide fully immersive educational settings that span distances in terms of location and accessibility, smart tutoring systems can deliver individualised feedback and resources.
AI as a Creative Partner in the Creative Arts
With tools that help create music, visual art, and even literary works, artificial intelligence (AI) is also creating waves in the creative arts. By analysing current works of art, AI algorithms are able to push the limits of human creativity by producing new compositions or providing artists with fresh ideas and inspiration.
AI and the Future of Work: Transformations and Opportunities
Creation and Transformation of Jobs
Even while AI can automate some work, it also changes and opens up new job prospects. The need for machine learning engineers, data scientists, and AI professionals has increased with the development of AI technologies. Furthermore, positions in governance, ethics, and policy related to AI are becoming increasingly important.
Retraining and Upskilling to Get Ready for the AI Era
Retraining and upskilling are crucial if one is to prosper in an AI-driven economy. Companies and educational institutions are providing training programs to assist employees in gaining the skills necessary for the AI era and in adjusting to new technology. The secret to surviving the changing nature of the workforce will be to prioritise flexibility and lifelong learning.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of AI: A Comprehensive Overview
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various aspects of our lives, from the way we work to how we interact with technology. Understanding both the advantages and disadvantages of artificial intelligence (AI) is crucial for leveraging its potential while addressing its challenges.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
- Automation of Routine Tasks: Artificial intelligence (AI) can automate repetitive and mundane tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex and creative activities. For example, in manufacturing, artificial intelligence (AI)-powered robots can perform assembly line tasks with high precision and speed.
- Optimized Processes: Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and optimize processes, improving efficiency in areas like supply chain management, logistics, and customer service.
Improved Decision-Making
- Data-Driven Insights: Artificial intelligence (AI) can process and analyze large datasets to provide actionable insights and support decision-making. In finance, artificial intelligence (AI) models can predict market trends and assist in investment strategies.
- Predictive Analytics: Artificial intelligence (AI) systems can forecast future trends and behaviors, helping businesses and organizations make informed decisions. For instance, in healthcare, artificial intelligence (AI) can predict patient outcomes and recommend personalized treatments.
Advancements in Healthcare
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment: Artificial intelligence (AI) can assist in early diagnosis of diseases through image recognition and analysis, leading to timely treatment and improved patient outcomes. Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms can detect anomalies in medical images that may be missed by human eyes.
- Personalized Medicine: Artificial intelligence (AI) enables personalized treatment plans based on individual gene
Innovation and Creativity
Creative Tools: Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to create art, music, and literature, offering new tools and inspiration for creative professionals. Artificial intelligence (AI)-generated content can push the boundaries of traditional art forms and explore novel creative possibilities.
Research and Development: Artificial intelligence (AI) accelerates research and development by simulating complex scenarios and generating new hypotheses, leading to faster breakthroughs in science and technology.
Disadvantages of AI
Job Displacement
- Automation Risks: While AI creates new job opportunities, it also poses a risk of job displacement, particularly in roles involving routine tasks. Automation can lead to the loss of jobs in industries such as manufacturing, customer service, and retail.
- Economic Inequality: The benefits of AI may not be evenly distributed, potentially widening the gap between skilled and unskilled workers and contributing to economic inequality.
Ethical and Bias Concerns
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems can inherit and perpetuate biases present in the data they are trained on, leading to discriminatory outcomes. For example, biased algorithms in hiring processes or law enforcement can reinforce existing prejudices.
- Lack of Transparency: Some AI models, particularly complex neural networks, operate as “black boxes,” making it challenging to understand how decisions are made. This lack of transparency can hinder accountability and trust in AI systems.
Security and Privacy Risks
- Data Security: AI systems often require access to large amounts of personal and sensitive data, raising concerns about data security and potential breaches. Protecting this data from unauthorized access is crucial.
- Privacy Invasion: AI technologies, such as surveillance systems and facial recognition, can intrude on individuals’ privacy and raise concerns about surveillance and data misuse.
Dependence and Overreliance
System Failures: AI systems are not infallible and can experience failures or malfunctions. Dependence on faulty AI systems can have significant consequences, especially in critical applications like healthcare and transportation.
Overreliance on AI: Excessive dependence on AI systems can lead to overreliance, where critical thinking and decision-making skills may diminish. This can be problematic in situations where human judgment is crucial.
Conclusion
The advantages and disadvantages of AI present a complex landscape that requires careful consideration. While AI offers numerous benefits, including enhanced efficiency, improved decision-making, and advancements in healthcare, it also brings challenges such as job displacement, ethical concerns, and security risks.
Navigating the future of AI involves leveraging its potential while addressing its drawbacks. By adopting responsible practices, fostering transparency, and promoting ethical development, we can harness AI’s capabilities for positive impact while mitigating its risks.
What Should We Do? Recommendations for Navigating the AI Landscape
As we move forward in an increasingly AI-driven world, it’s essential to take proactive steps to maximize the benefits of AI while addressing its challenges. Here are some key recommendations:
- Promote Ethical AI Development
- Foster Transparency: Encourage the development of AI systems that are transparent and understandable. This includes implementing explainable AI techniques that allow users to comprehend how decisions are made.
- Address Bias: Prioritize the elimination of biases in AI algorithms by diversifying training data and involving diverse teams in AI development. Regularly audit AI systems for fairness and accuracy.
- Prepare for Workforce Changes
- Upskill and Reskill: Invest in education and training programs to help workers transition into new roles created by AI advancements. Emphasize skills that complement AI technologies, such as creative problem-solving and emotional intelligence.
- Support Job Transition: Develop policies and support systems for individuals displaced by automation, including career counseling and financial assistance.
- Ensure Data Security and Privacy
- Implement Robust Security Measures: Use advanced security protocols to protect sensitive data used by AI systems. Regularly update security practices to counter emerging threats.
- Respect Privacy: Establish clear guidelines for data collection and usage, ensuring that AI applications respect user privacy and comply with regulations like GDPR.
- Encourage Responsible AI Use
- Promote Human Oversight: Ensure that AI systems are used as tools to support human decision-making rather than replacing it. Maintain human oversight in critical areas such as healthcare and law enforcement.
- Foster Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between technologists, policymakers, and ethicists to develop guidelines and standards for AI development and deployment.
- Stay Informed and Adapt
- Monitor AI Developments: Stay informed about advancements and emerging trends in AI. Adapt strategies and practices as technology evolves to remain competitive and responsible.
- Engage in Public Discourse: Participate in discussions about the societal impacts of AI and contribute to shaping policies and regulations that govern AI use.
By taking these steps, we can navigate the complexities of AI, harness its potential for positive change, and address the challenges it presents. Embracing responsible practices and staying informed will help ensure that AI benefits society as a whole.
Thank you for reading.